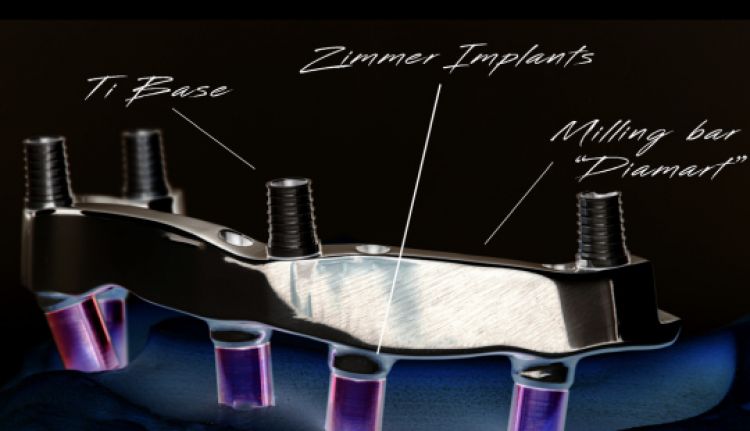
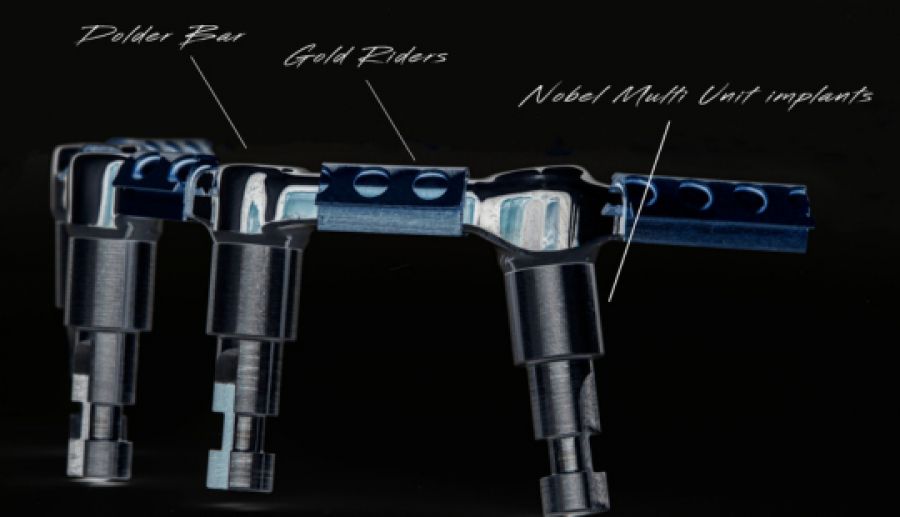
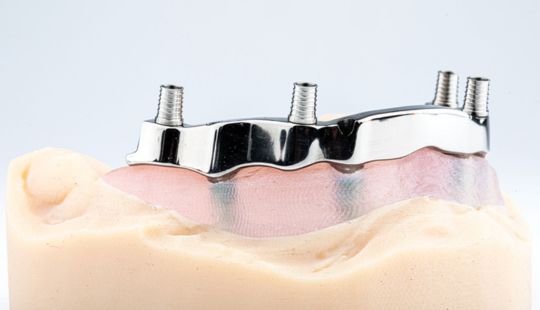
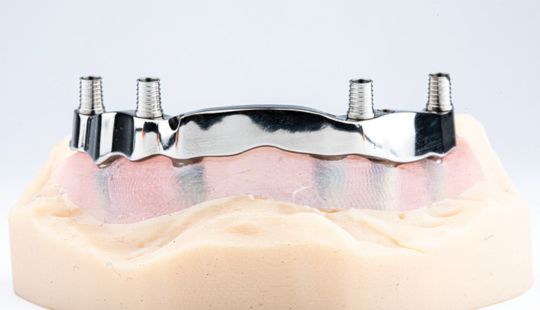
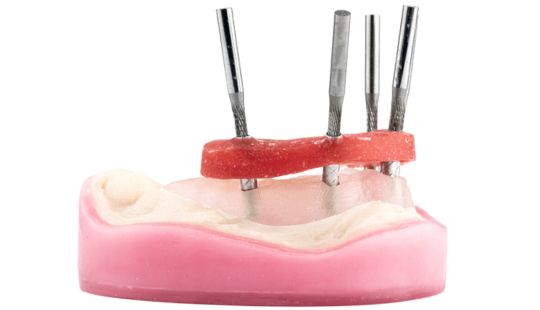
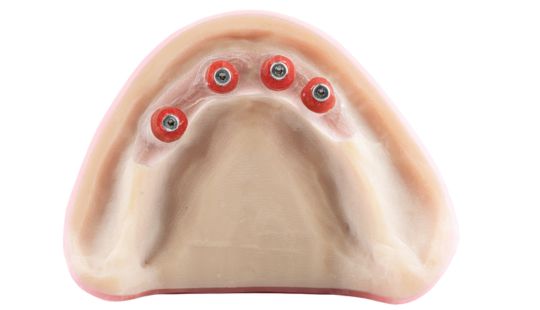
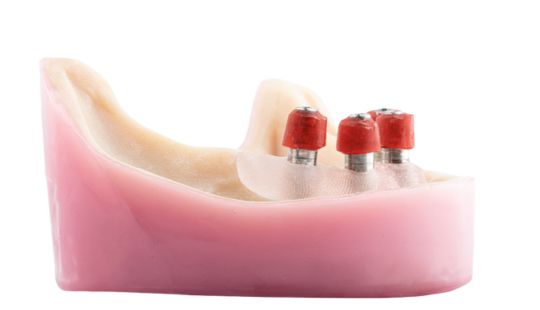
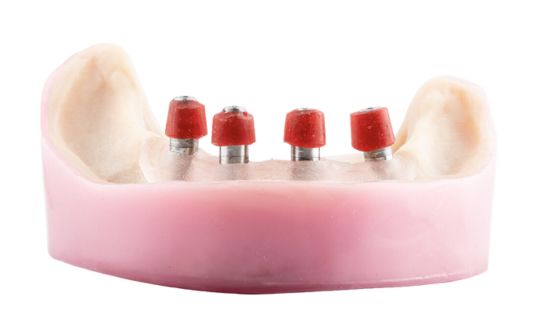
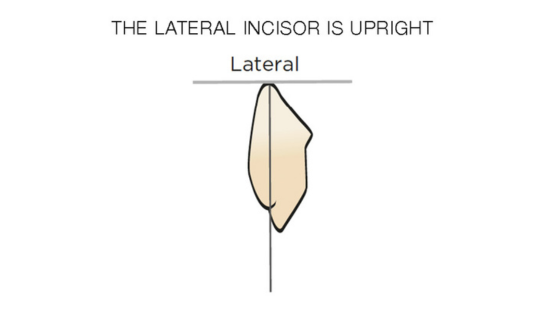
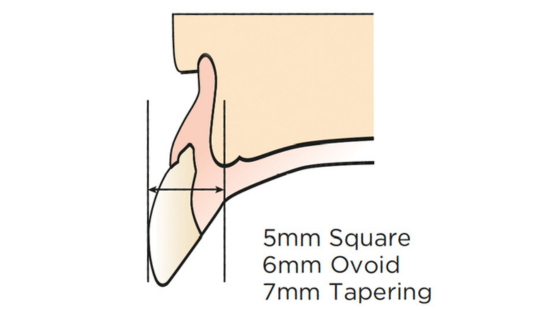
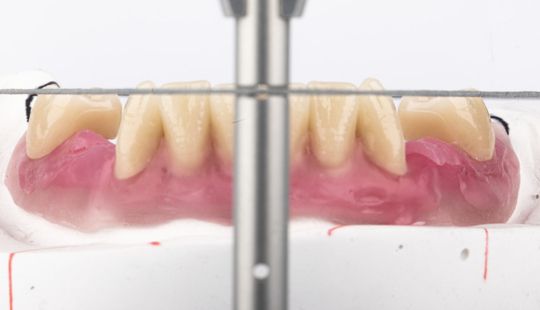
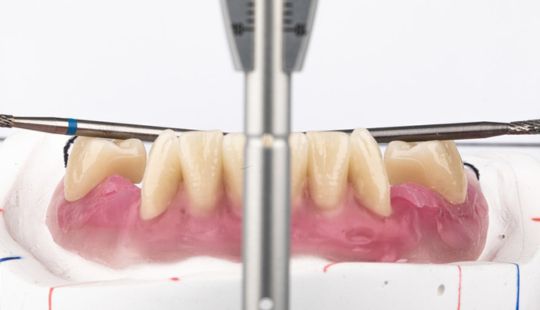
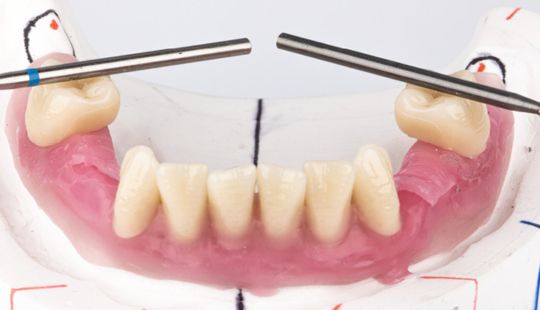
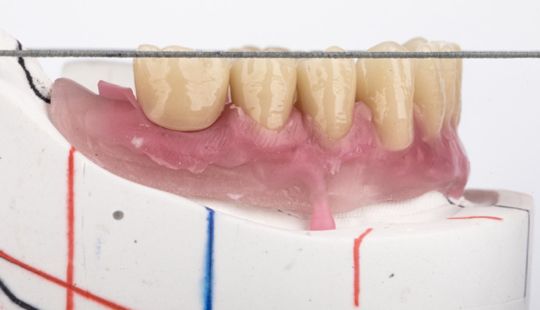
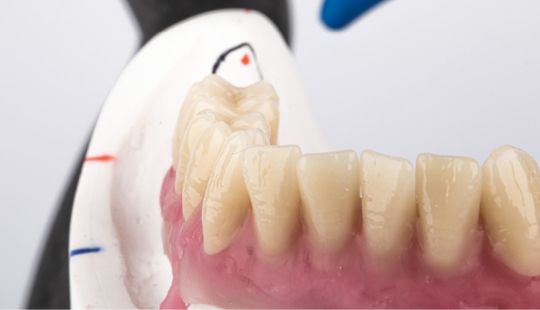
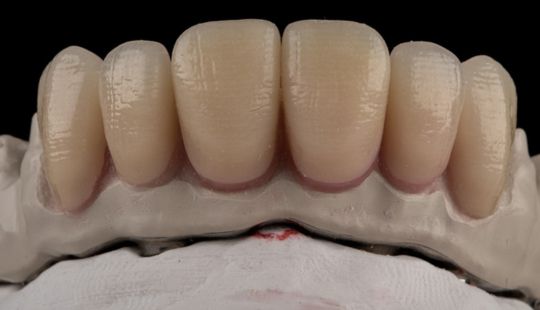
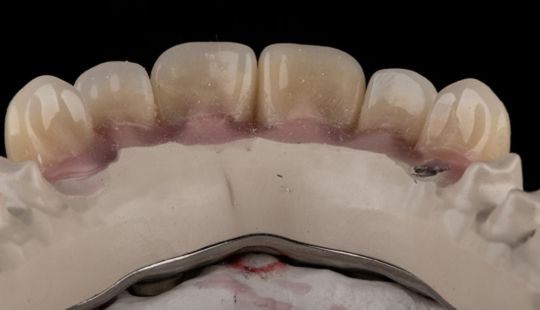
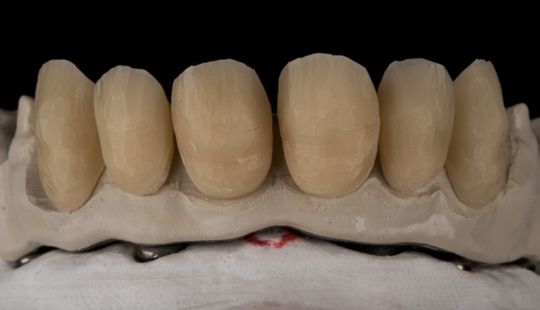
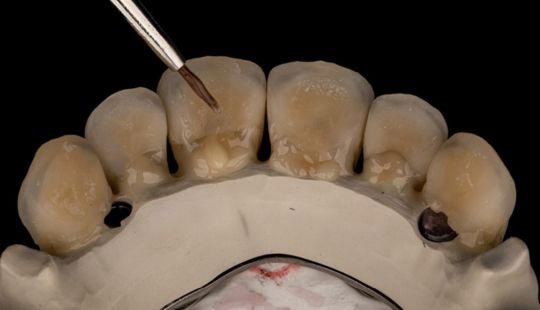
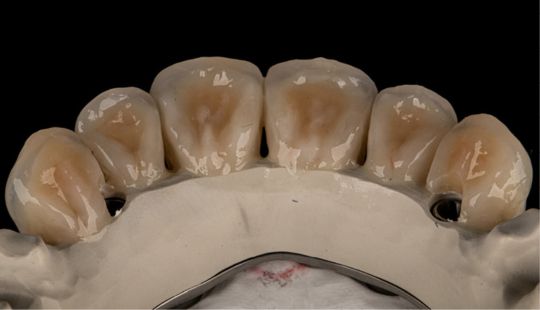
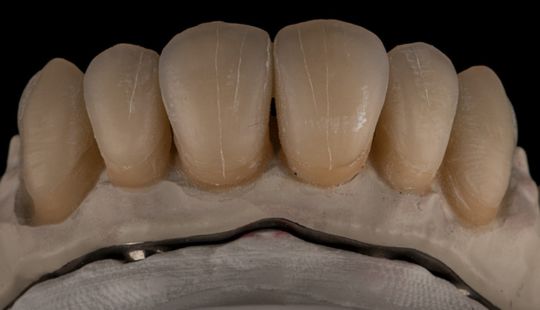
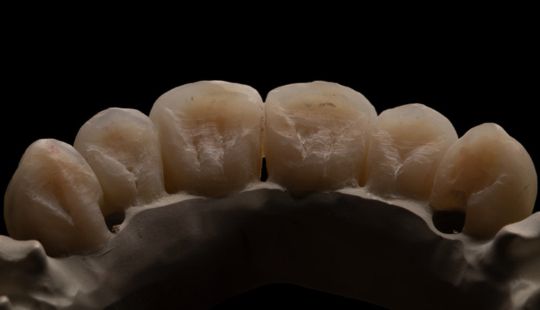
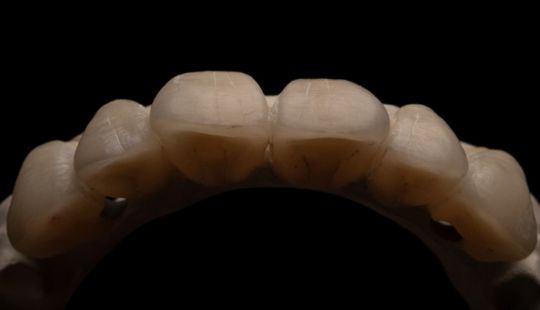
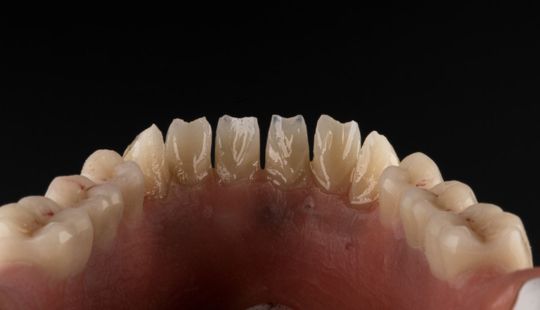
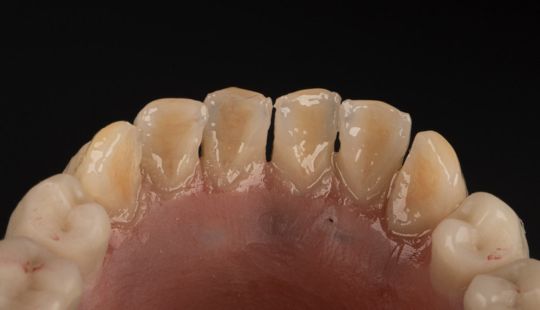
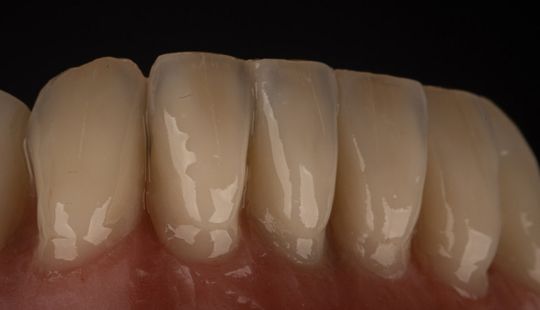
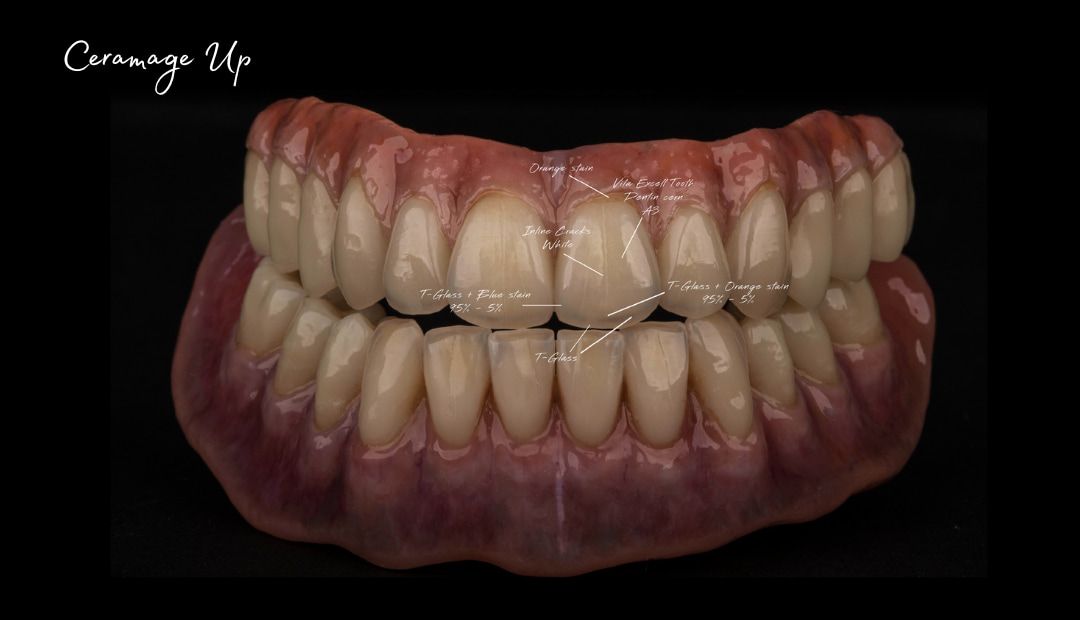
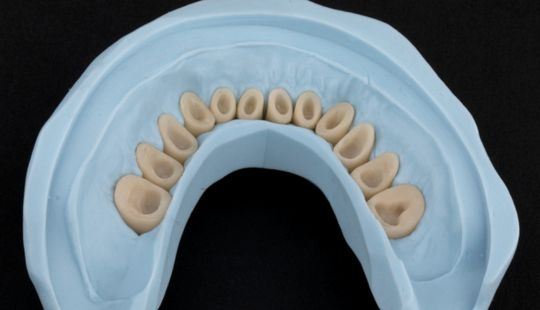
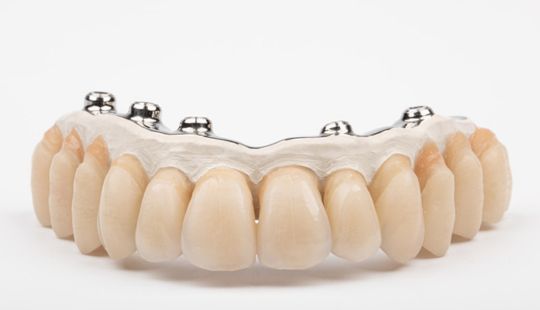
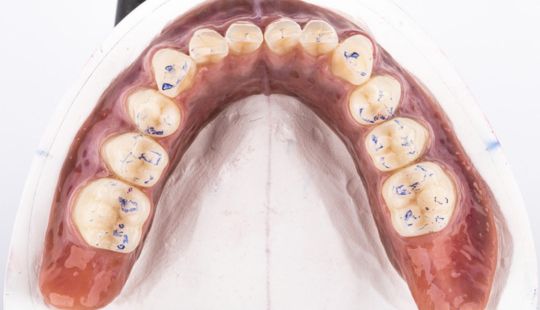
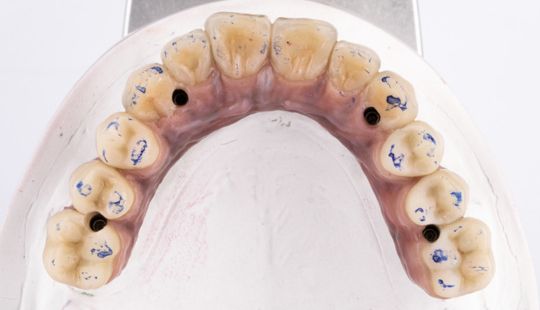
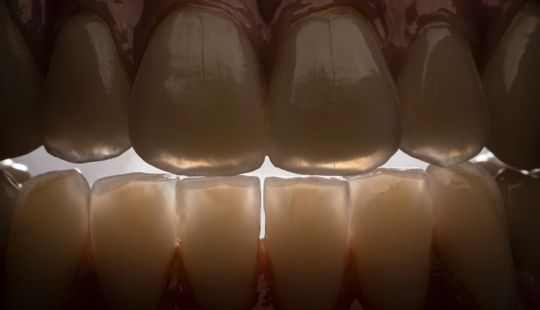
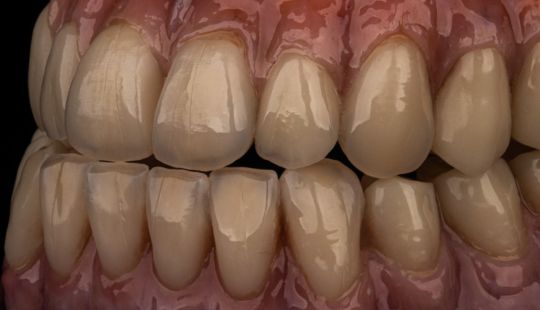
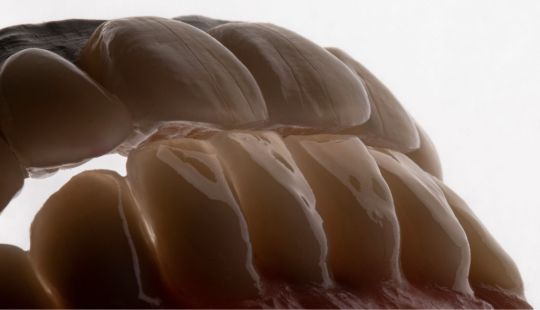
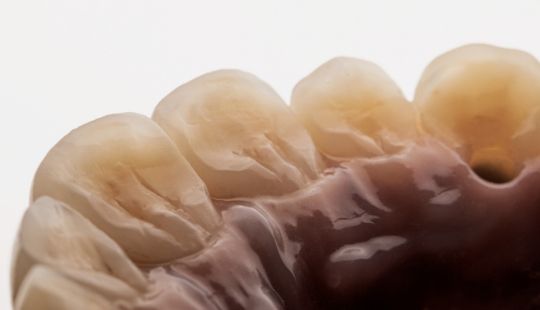
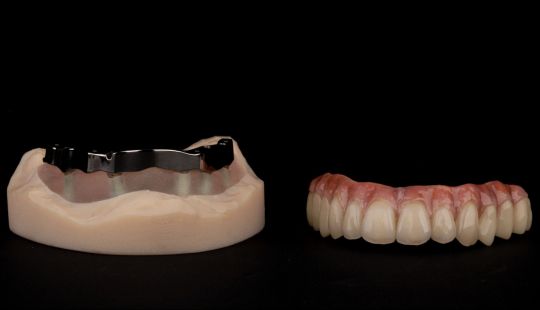
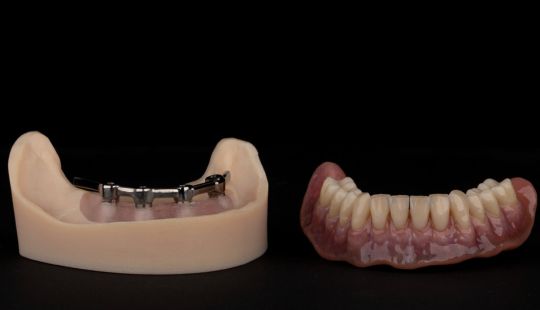
Morphology (Mold): 1. Gender: male – rugged with square teeth & bold central incisors. female – pronounced curvatures, rounded point angles 2. Personality: vigorous or delicate “Personality tooth” The maxillary lateral incisors vary more in size, form and position than any other tooth 3. Age: Young: Tapered, ovoid, rounded teeth. Old: Square, sharp corners
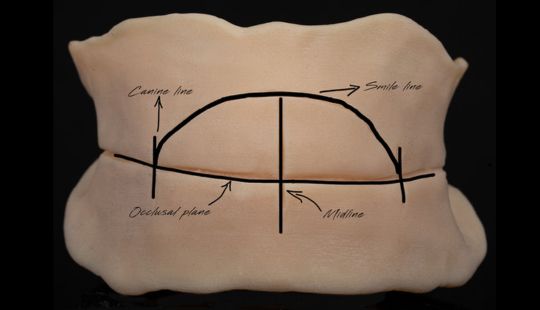
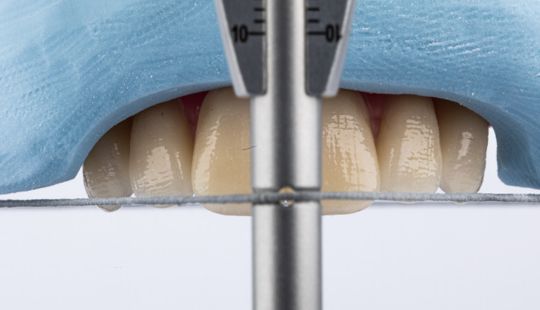
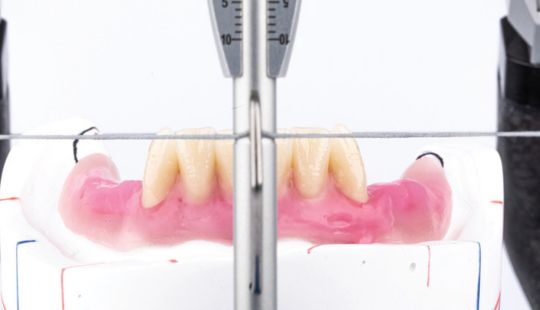
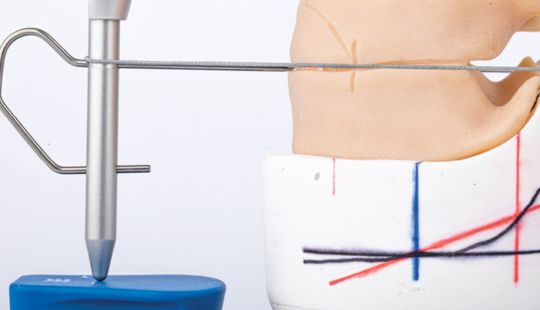
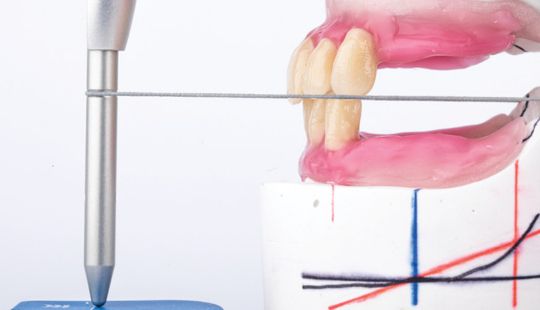
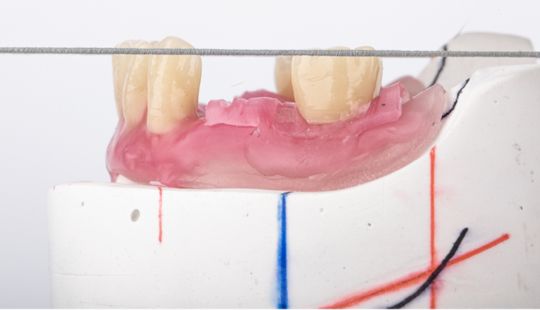
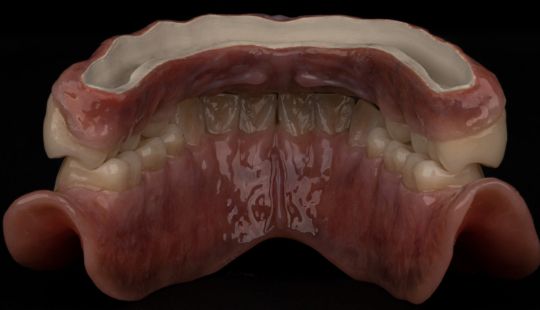
Size: 1. Must harmonize with face and arch size. 2. Any disproportion in arch size influences the length, width and position of the teeth. 3. Vertical distance between the ridges – use a tooth long enough to minimize the display of the denture base. 4. Mark high lip line and canine lines on the occlusion rim at the time the jaw relations are recorded. These guide lines provide information about the gingival-incisal length and total mesiodistal width of the maxillary six anterior teeth. 5. Shape and contour the wax rim so that it mimics the shape and contours of the finished denture with the anterior teeth. 6. The wax rim should extend 1-2 mm below the lip line. 7. Mark the canine line at the corner of the lips and measure the distance with a flexible ruler.
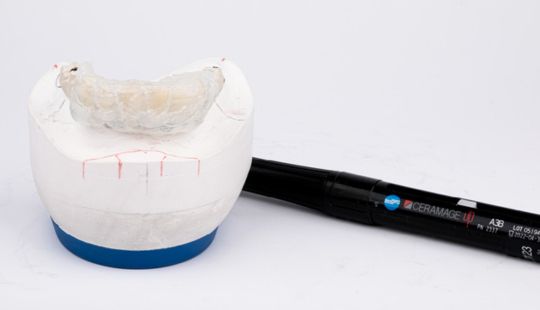
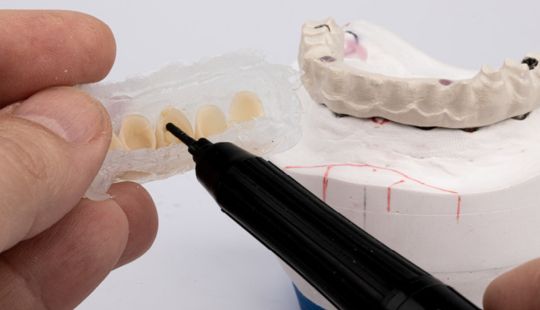
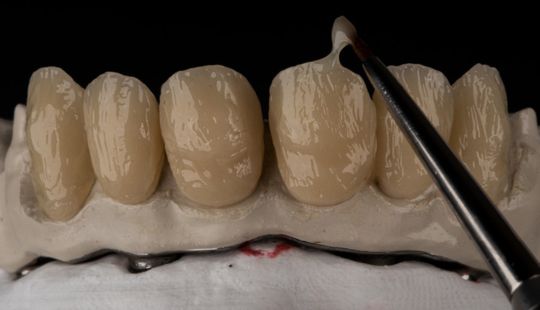
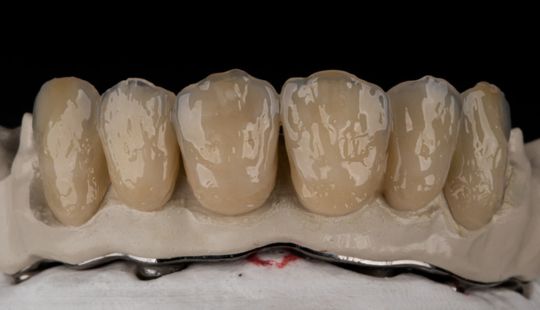
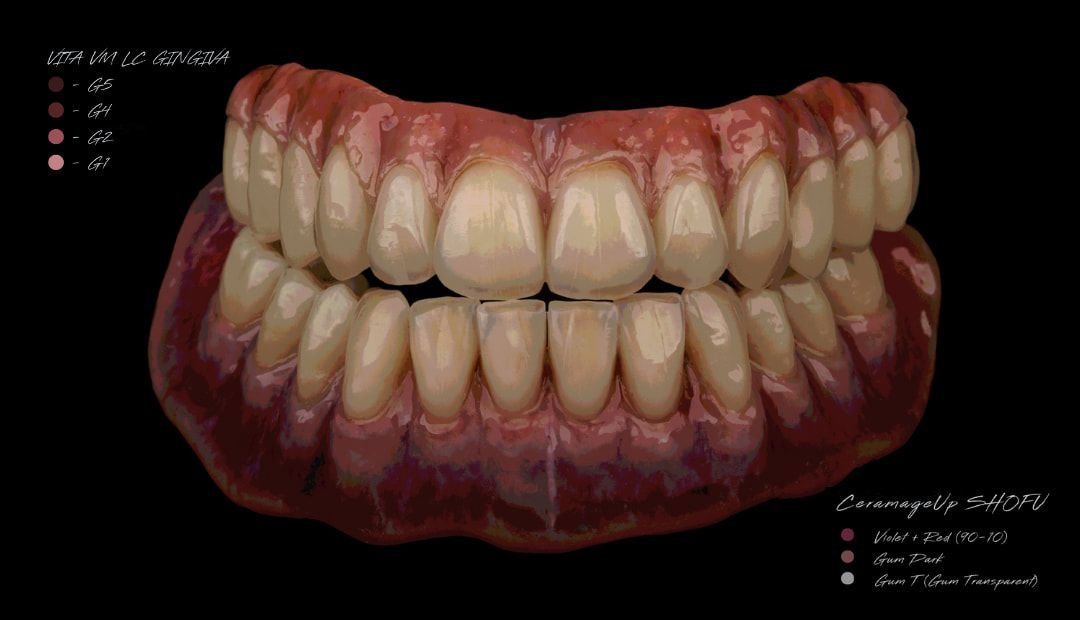
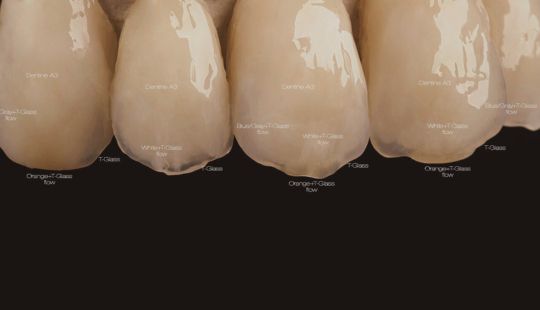
Color: Guides 1. Complexion 2. Hair color 3. Eye color 4. Age 5. Personality & activity 6. Patient desires 7. Need to educate patients
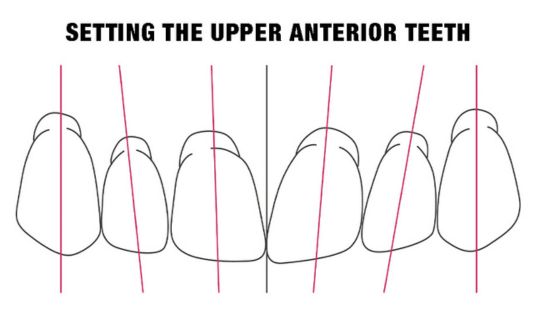
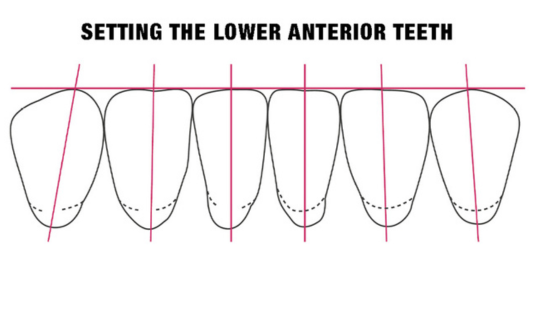
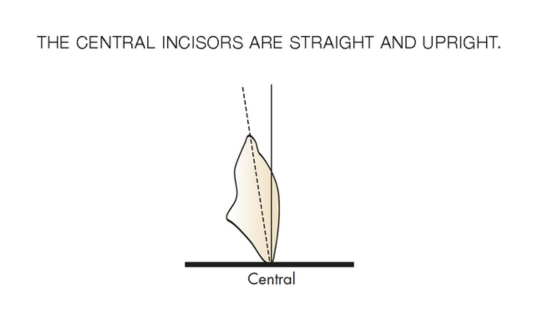
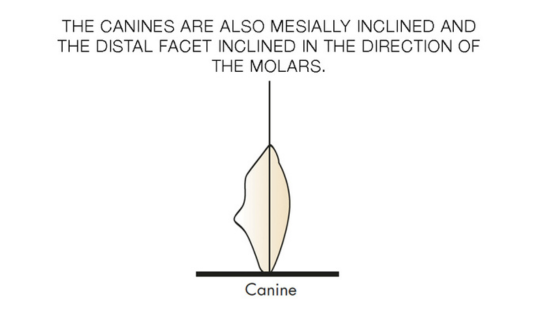
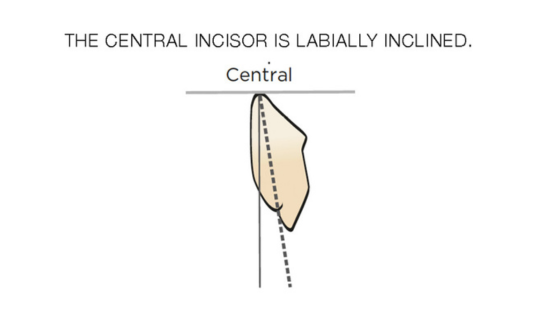
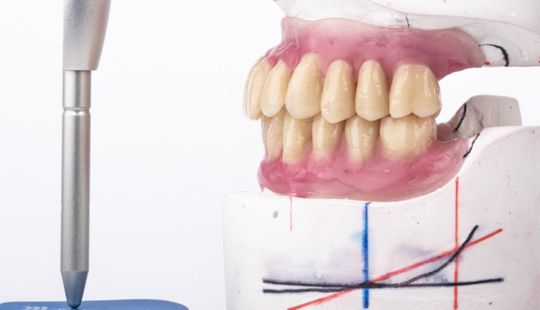
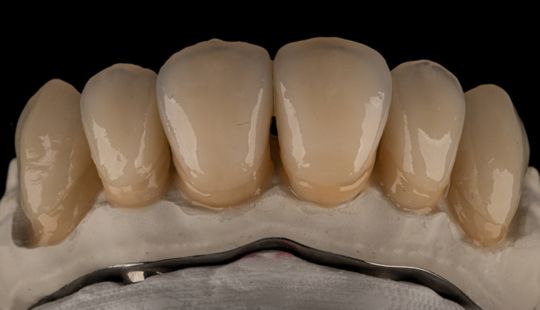
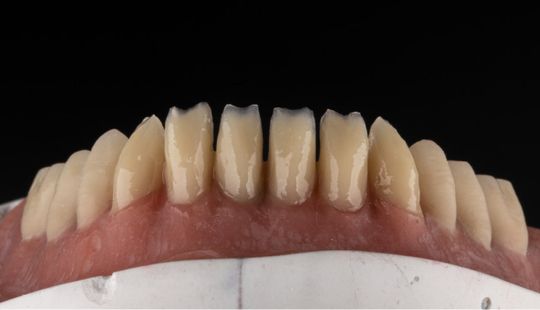
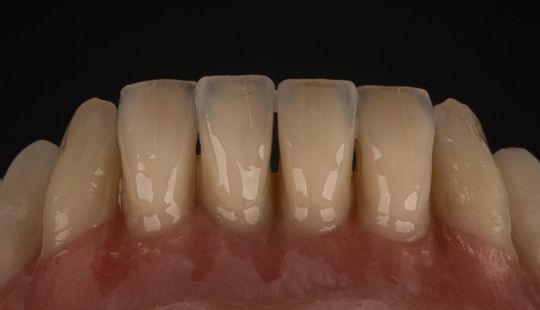
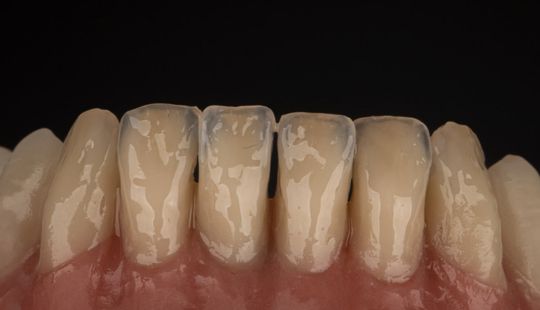
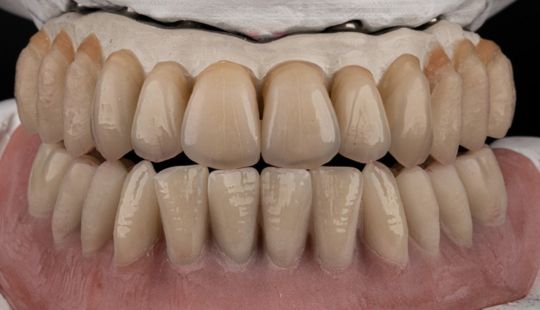
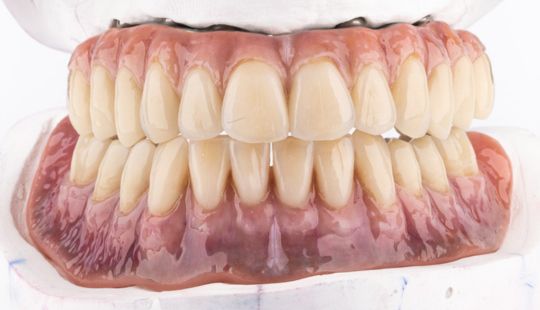
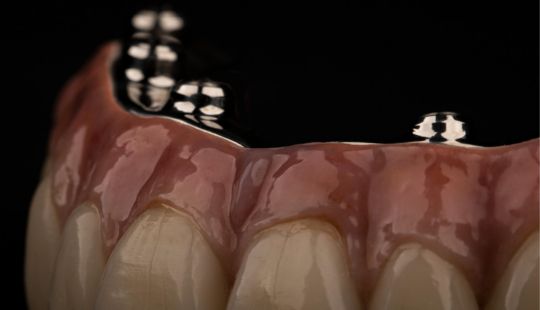
Tooth Placement: Positioned in the same general area on the natural teeth. This position was tentatively established during the clinical refinement of the maxillary occlusal rim to provide adequate lip support and proper phonetics. Used to its maximum potential when accomplished at chairside. The arrangement has to fulfill certain biomechanical needs as well as esthetic ones.
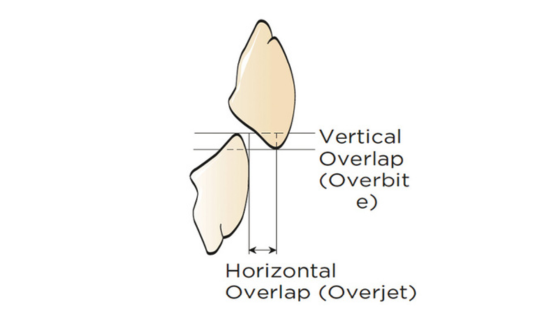
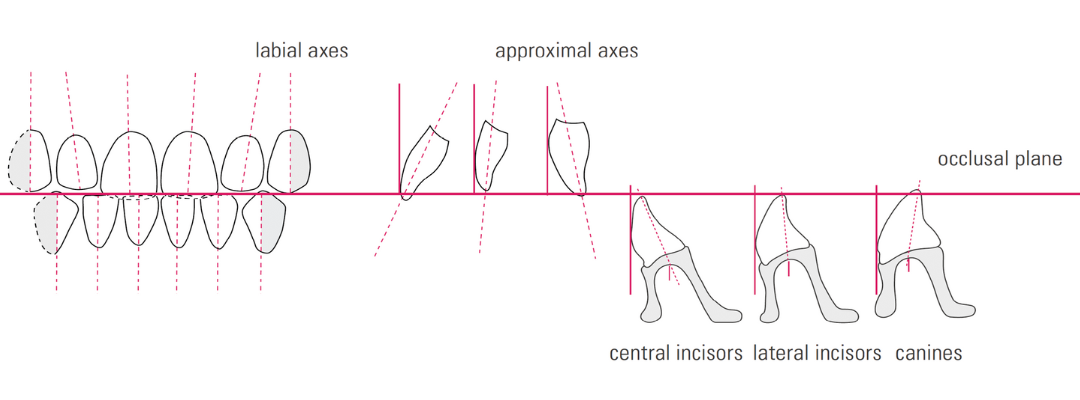
Factors: 1.Midline 2.Lip support 3. Vermilion border 4.Phonetics- f, v, s sounds 5. Buccal corridor 6. Canine eminance- arch type, square, tapered, ovoid 7. Incisal papilla- to labial of central incisor 8-10 mm 8. Vertical and horizontal overlap- 1.5 mm. 9. Generally, 1-2 mm of the incisal portion of the maxillary central incisor is visible below the relaxed lip. 10. Smile line- follow contour of lower lip. 11. Occlusal Plane.